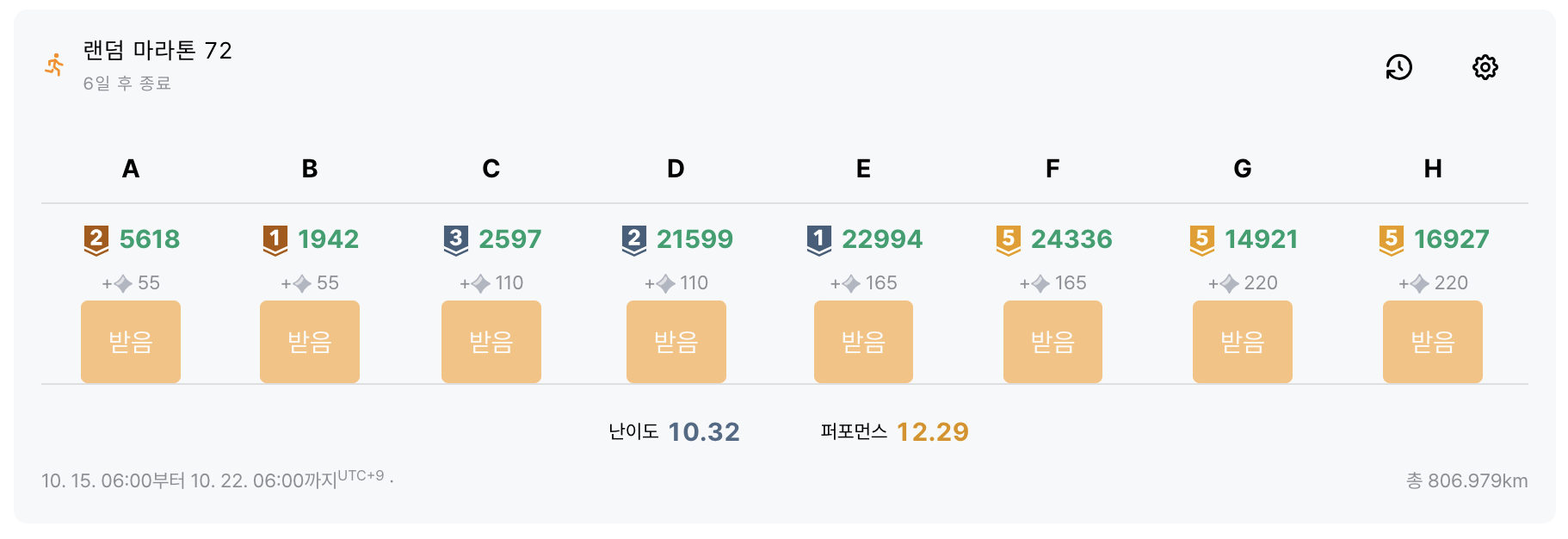
A. 공약수
 브론즈 II
브론즈 II
유클리드 호제법으로 공약수를 구한 뒤 약수를 출력하면 됩니다.
1 | |
B. 디지털시계
 브론즈 I
브론즈 I
문제에서 요구하는 것을 잘 구현하면 됩니다.
1 | |
C. 줄자접기
 실버 III
실버 III
줄자의 길이를 $l$이라 하고 수직선 위의 두 점 $0$과 $l - 1$을 잇는 선분으로 생각해 봅시다.
점 $m$을 기준으로 반으로 접으면 줄자의 길이는 $\max(m, l - m)$이 됩니다.
접는 점을 원점인 $0$으로 재조정하면 $m$보다 왼쪽에 있는 점 $x$는 $m - x$, 오른쪽에 있는 점 $y$는 $y - m$으로 바꿀 수 있습니다.
1 | |
D. 아이템 배치하기
 실버 II
실버 II
강화력이 큰 것부터 내림차순으로 배치하는것이 이득입니다.
현재까지 강화된 아이템의 최대 인덱스를 관리하는 방법으로 $\mathcal{O}(N)$에 해결할 수 있습니다.
강화력이 $0$이면 break하도록 하면 현재까지 봤던 아이템들은 모두 강화된 상태이므로 강화된 아이템의 최대 인덱스가 $N$이 넘어가면 $N$개가 모두 강화됨을 알 수 있습니다.
1 | |
E. 이미지 축소
 실버 I
실버 I
연속으로 열이 같은 모든 경우의 최대 공약수, 행이 같은 모든 경우의 최대 공약수를 각각 구하면 가장 큰 $i, j$를 구할 수 있습니다.
1 | |
F. 가희와 무궁화호
 골드 V
골드 V
그냥 열심히 구현하면 됩니다…
다음 날로 넘어가는 부분을 구현할 때 주의합시다.
1 | |
G. 용액 합성하기
 골드 V
골드 V
두 포인터로 $\mathcal{O}(N)$에 해결할 수 있습니다.
$l = 0$, $r = N - 1$로 초기화합시다.
$A_l + A_r < 0$인 경우 합을 늘려야 하므로 $l$을 증가시킵니다.
$A_l + A_r > 0$인 경우 합을 줄여야 하므로 $r$을 감소시킵니다.
1 | |
번외로, 이분 탐색으로도 해결할 수 있습니다.
1 | |
H. 배열 돌리기 2
 골드 V
골드 V
$(i, j)$에 있는 수를 $(i, j + c)$로 옮기고 나머지를 왼쪽으로 한칸씩 당기는 방법을 생각해 봅시다.
$(i, j)$와 $(i, j + 1)$를 교환하고, $(i, j + 1)$와 $(i, j + 2)$를 교환하고… 를 반복하면 됩니다.
따라서 반시계방향으로 회전하는 것은 시계방향으로 교환하는 행위와 같습니다.
회전해야 할 길이로 $R$을 나눈 나머지만큼 회전하면 시간 복잡도 $\mathcal{O}(N^3)$ 정도에 해결할 수 있습니다.
1 | |